Last Updated on November 12, 2025
If you’ve ever Googled something and noticed a small box titled “People also search for” beneath a result — you’ve seen one of Google’s most valuable, yet underrated, SEO signals: PASF.
Contrary to older belief, this feature is no longer exclusively triggered by a user bouncing back from a page. While the bounce-back still creates the most prominent placement for PASF (directly under the clicked result), in 2025, PASF now appears dynamically even during the first search for many queries, reflecting how Google continuously refines its understanding of related user intent.
Let’s explore what PASF is, how it works, and how you can leverage it for powerful SEO and content strategy.
What Is “People Also Search For” (PASF)?
People Also Search For (PASF) is a Google feature that displays related search queries to help users explore a topic more deeply. These suggestions often appear:
- Under a specific search result snippet.
- On mobile and desktop search interfaces.
- Sometimes even directly in the “Related searches” section at the bottom of the page.
In essence, PASF is Google’s way of saying:
“People looking for what you searched also wanted to know about these topics.”
How PASF Works in 2025
Previously, PASF was thought to trigger only when users clicked a result and then quickly returned to the SERP (a signal of dissatisfaction or curiosity).
But Google’s recent updates have changed this behavior.
Now, PASF is generated dynamically based on search intent clusters — even before a click happens.
This is powered by:
- Semantic search algorithms
- Natural language processing (NLP)
- User intent modeling
These improvements help Google predict related subtopics likely to interest the user, making PASF a real-time reflection of user journeys instead of just bounce data.
Why PASF Matters for SEO
PASF gives SEO professionals and content marketers a window into user intent — the “why” behind a search query.
Here’s why it’s powerful:
- Reveals Search Intent Variations
PASF shows what else users want to know around your keyword — helping you map informational, navigational, and transactional intent. - Identifies Content Gaps
If your page covers the primary query but misses the related PASF questions, your content may not satisfy all intent signals — and might rank lower. - Enhances Topical Authority
By addressing PASF topics, you create semantically rich content that Google associates with authority on a given subject. - Improves Dwell Time and Engagement
Answering PASF queries within your article reduces pogo-sticking and keeps readers engaged longer. - Feeds Your Keyword Expansion Strategy
PASF terms often contain low-competition, high-intent long-tail keywords ideal for blog topics and cluster pages.
Where You’ll See PASF in Action
You can observe PASF in several locations:
- SERP Snippets – Beneath individual search results
- Mobile SERPs – Inline “People also search for” carousels
- Knowledge Panels – Related entities and searches
- YouTube Search Results – Related video queries
- Google Discover Feeds – Predictive query recommendations
Example: PASF in Action
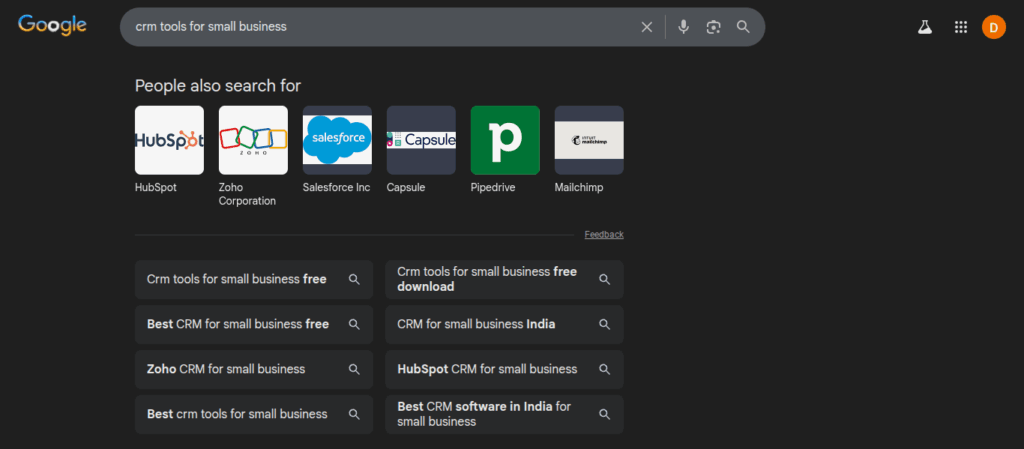
Let’s say you search for “Best CRM software 2025.”
Google might show:
- People also search for:
- “CRM tools for small business”
- “HubSpot alternatives”
- “Sales automation software”
- “CRM trends 2025”
This tells you that:
- Users are comparing tools.
- They want affordable or SMB-focused CRMs.
- They’re interested in automation and trends.
As a content marketer, you can use this insight to create multiple blog angles, such as:
- “Top 10 HubSpot Alternatives for Small Businesses”
- “Best Sales Automation Tools in 2025”
- “Future of CRM: What’s Changing in 2025”
How to Find PASF Keywords
You can discover PASF terms using any of these methods:
1. Manual Search
- Simply perform a Google search.
- Scroll through results and note PASF boxes under listings.
2. Browser Extensions
Tools like Keyword Surfer or SEO Minion highlight PASF terms directly in SERPs.
3. SEO Platforms
Platforms like Ahrefs, Semrush, and RankYak now show PASF data alongside “People Also Ask” (PAA) for intent analysis.
4. Custom Scraping (For Developers)
If you’re technical, you can use Playwright or Puppeteer scripts to fetch PASF data in bulk for content planning.
PASF vs PAA vs Google Autocomplete
Although People Also Search For (PASF), People Also Ask (PAA), and Google Autocomplete may look similar, each serves a unique purpose in Google’s ecosystem.
PASF shows related search topics or entities that users commonly explore after viewing a particular result.
It helps uncover broader or adjacent user intents connected to your main keyword.
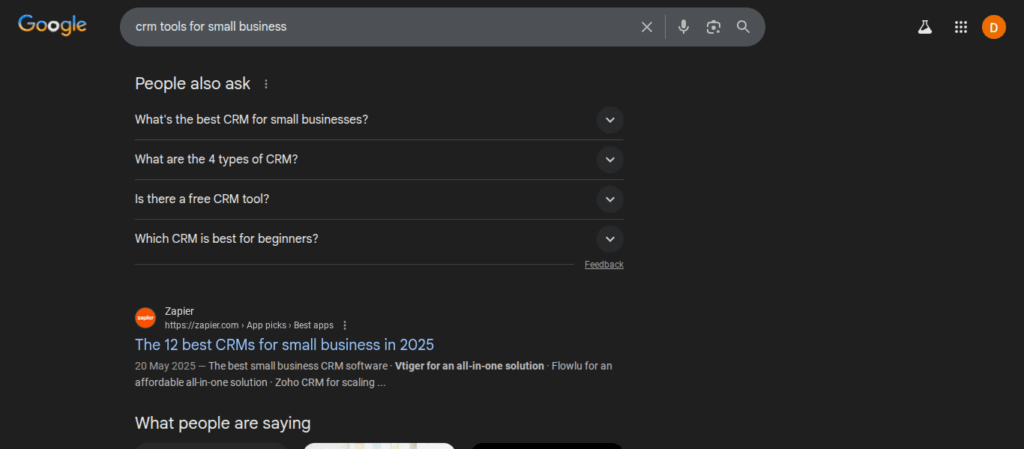
PAA displays a set of expandable questions that other users frequently ask about your topic. It helps you identify question-based keywords and FAQ opportunities for featured snippets.
Autocomplete predicts and completes search queries in real time as you type. It helps you discover trending, long-tail, and intent-rich keyword ideas before users even hit “search.”
| Feature | People Also Search For (PASF) | People Also Ask (PAA) | Google Autocomplete (Suggest) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Where It Appears | Below a search result or in SERP panels | In collapsible “question boxes” | In the search bar dropdown while typing |
| Purpose | Suggest related or next-step queries | Display common user questions and answers | Predict and complete queries as you type |
| When It Appears | Even during first searches | Always visible for question-based queries | While typing the query (pre-search) |
| Data Source | User intent models + semantic relationships | Knowledge Graph + Q&A database | Aggregated from trending and historical searches |
| Content Type | Related topics, entities, or keywords | Specific questions and answers | Partial or predictive keyword phrases |
| SEO Use Case | Find related topics and internal linking ideas | Build FAQ sections, target featured snippets | Identify trending or new keyword opportunities |
| User Interaction | Static (clickable links) | Interactive (expandable answers) | Predictive (real-time typing suggestions) |
| Example | “People also search for: CRM tools for startups” | “People also ask: What is the best CRM for small business?” | Typing “best CRM” shows “best CRM for real estate,” “best CRM 2025” |
How to Use PASF Data for SEO Strategy
1. Create Topical Clusters
Group PASF terms around your main keyword.
Example:
Main keyword — Email marketing
PASF terms — “email automation tools”, “email subject line examples”, “email marketing strategy”
Each can become a subtopic blog linking back to your pillar content.
2. Optimize Existing Pages
Add a section addressing 2–3 PASF queries at the end of your post (similar to FAQs).
This increases semantic relevance and featured snippet potential.
3. Expand Internal Linking
Use PASF keywords as anchor texts to connect related posts — improving both UX and crawl depth.
4. Plan Video or Visual Content
PASF also informs YouTube video titles and Pinterest post ideas — since Google often mirrors trends across platforms.
5. Monitor SERP Shifts
PASF changes dynamically based on search patterns.
Tracking these shifts helps you detect new content opportunities early.
PASF and Semantic SEO: The Connection
Google’s modern algorithm focuses less on exact keywords and more on semantic meaning — how concepts are related.
PASF is a live reflection of this.
If you analyze PASF terms for your niche, you’ll see they’re often:
- Synonyms or contextual expansions of your keyword.
- Part of broader entity-based relationships.
By creating content that mirrors these relationships, you align directly with how Google interprets topics in 2025.
PASF + PAA + Related Searches = Full Topic Coverage
To build complete topical authority, combine:
- PASF (related journeys)
- PAA (common questions)
- Related Searches (bottom-of-page expansions)
Example:
For “digital marketing trends 2025”:
- PASF might show → AI content tools, social media automation, SEO in 2025
- PAA might show → What are the top digital marketing trends in 2025?
- Related searches might show → future of marketing, automation in ads
Together, they form a map of what users want to know.
PASF in 2025: What’s New
- AI-Based Intent Grouping
Google clusters PASF based on semantic similarity, not just keyword overlap. - Predictive Appearance
PASF can now appear during the first query due to real-time personalization. - Entity Recognition
PASF now relates to brands, people, and products (not just phrases). - Featured Snippet Integration
Some PASF queries now directly pull from featured snippets or Google Perspectives. - Localized PASF Suggestions
You may see different PASF results for the same query depending on your location.
How Marketers Can Leverage PASF in 2025
- Content Planning: Build blog clusters from PASF data.
- Product Page SEO: Add PASF keywords to product FAQs or comparison tables.
- Voice Search Optimization: PASF often overlaps with spoken queries.
- Competitor Benchmarking: Check which PASF terms competitors target — and find untapped ones.
- Ad Copy Enrichment: Use PASF insights to match ad keywords to actual user phrasing.
Pro Tip: Combine PASF With Search Console Data
Export your site’s Search Console queries, then cross-match them with PASF terms for your main topics.
This helps you identify:
- Keywords Google already ranks you for.
- Related PASF terms you don’t rank for yet — i.e., your next content opportunities.
- Top AI Marketing Tools in 2026 - December 2, 2025
- Best SEO Content Optimization Tools - November 13, 2025
- People Also Search For (PASF): The Complete 2025 Guide to Smarter SEO Optimization - November 11, 2025