Last Updated on September 19, 2025
What is NLP?
Natural Language Processing (NLP), is a branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on the interaction between computers and human language. It involves the development of algorithms and systems that can read, understand, interpret, and mimic human languages in a valuable and meaningful way. NLP aims to bridge the gap between human communication and computer understanding, enabling machines to process and analyze large amounts of natural language data. This technology plays a crucial role in various applications, from search engines to voice assistants, making it an essential field in the advancement of AI and machine learning.
How Does NLP Work?
NLP works by combining computational linguistics with machine learning. It involves processing and analyzing natural language data to understand the context, sentiment, and intent behind human language. This process often includes tasks like tokenization, part-of-speech tagging, and named entity recognition, allowing computers to break down and interpret complex language structures. Through these techniques, NLP enables machines to understand, interpret, and respond to human language in a meaningful way.
Tasks of NLP
In NLP, the process of understanding human language involves several critical tasks:
Tokenization: This is the process of breaking down text into individual elements, called tokens. For example, in the sentence “Natural Language Processing is fascinating,” each word is a token.
Part-of-Speech Tagging: This task involves identifying each token’s grammatical role – such as noun, verb, adjective. In the sentence “Birds fly south in winter,” ‘Birds’ is a noun, ‘fly’ is a verb, and ‘south’ is a noun.
Named Entity Recognition (NER): NER identifies and classifies named entities within text into predefined categories like names of persons, organizations, locations. For instance, in “Albert Einstein was born in Germany,” ‘Albert Einstein’ would be recognized as a person, and ‘Germany’ as a location.
How to use Google NLP tool for SEO
In the ever-evolving world of SEO, understanding and leveraging Natural Language Processing (NLP) is becoming increasingly crucial. NLP, at its core, is about understanding human language nuances. NLP helps in comprehending and optimizing content for search engine algorithms like Google’s BERT and SMITH, enhancing the relevance and visibility of web content. SEO isn’t just about keywords anymore. It’s about understanding context, intent, and user behavior. NLP aids in analyzing these aspects, making it a valuable tool for SEO professionals.
Step 1 : Find the right keyword to rank for
It is the most crucial step for ranking, so that we have a fair idea about search volume and competition.
Search volume you can easily extract out from Google Ads and google will show you all of your competition upon searching the keyword.
Step 2: Find the top ranking website
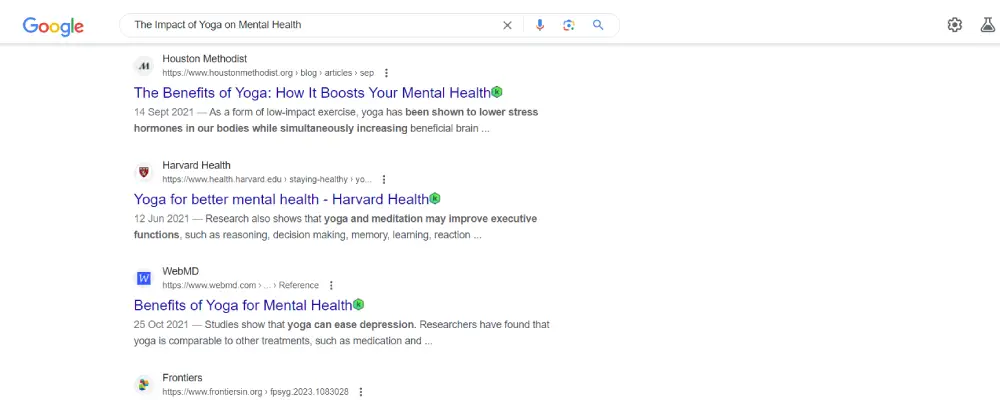
Now do a google search for the selected keyword and click on the number 1 organic result. We will be analyzing the content of the top ranking website using Google’s natural language processing tool. Since this site is ranking #1 organically, it likely contains effective keyword usage and other optimization factors that Google deems valuable. By leveraging Google’s machine learning technology, we can uncover the elements that contribute to this page’s high ranking.
Step 3: Using Google Natural Language API
Go to Google Natural Language, and copy paste the entire content from the number one ranking site and click Analyze.
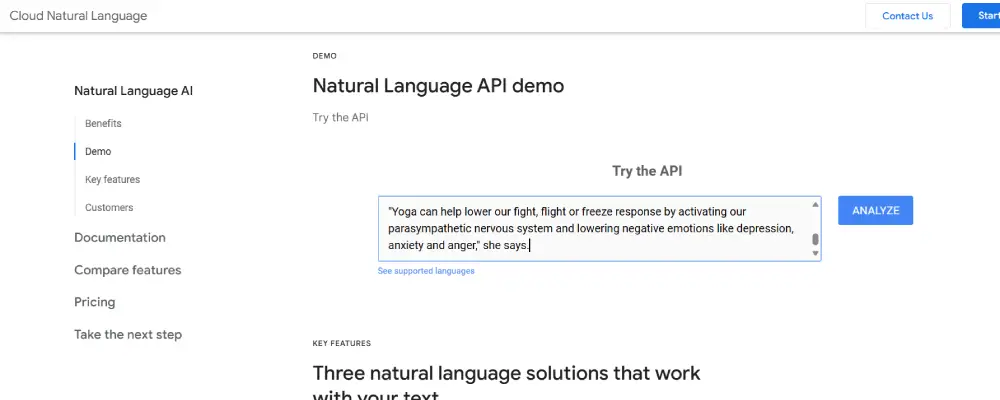
It divides the content into four categories:
1. Entities
Note down the keywords along with their groupings such as price, number, address, location. In the realm of SEO, understanding and leveraging entities can significantly enhance content optimization. Entities refer to distinct, well-defined terms or concepts within a text, such as names, places, brands, or other specific nouns.
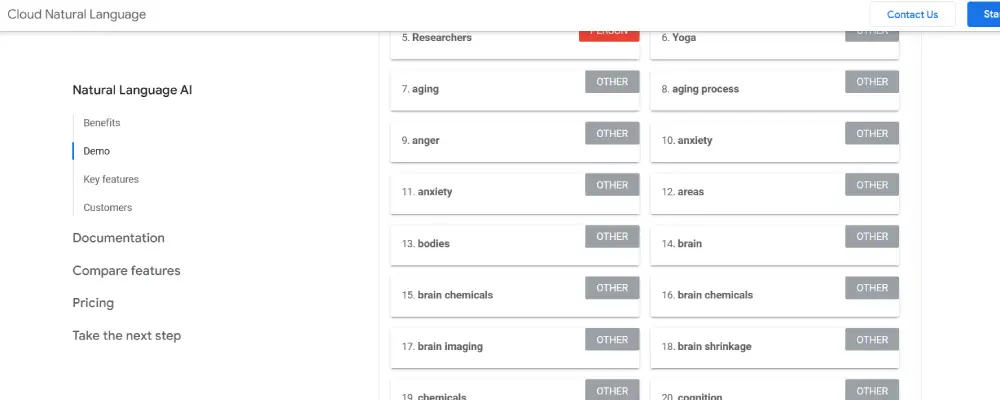
Entities are crucial because search engines like Google use them to understand the content’s subject matter and context. By recognizing and prioritizing these entities, search engines determine the relevance of content to specific search queries. The salience of an entity indicates its prominence within the content, helping search engines grasp the primary focus and nuances of the text.
Consider a blog post about “The Health Benefits of Mediterranean Diet.” In this post, entities might include “Mediterranean Diet,” “olive oil,” “heart health,” and “Omega-3 fatty acids.” Among these, “Mediterranean Diet” would likely have the highest salience, being the central topic of the article. Secondary entities like “heart health” and “Omega-3 fatty acids” support and enrich the primary topic, indicating to search engines the depth and scope of the content.
2. Sentiment Analysis for Content Tone
Sentiment Analysis in SEO refers to the process of evaluating the emotional tone of content, which can be positive, negative, or neutral. This can be helpful for evaluating the featured snippet for a keyword to see if Google is surfacing more positive or negative content. Businesses also use sentiment analysis to determine if customer reviews on their own websites have a positive or negative tone overall. Breaking down text by sentiment provides insight into how customers feel about products and services.
The emotional tone of content can significantly influence user interaction and perception. Search engines, recognizing this, consider sentiment as a factor in determining content relevance and quality. By analyzing and aligning the sentiment of your content with the expected user sentiment, you can improve both user experience and SEO performance.
Imagine an article titled “The Impact of Yoga on Mental Health.” This article is likely to have a positive sentiment, discussing the benefits of yoga on mental well-being. The positive tone aligns with what readers searching for this topic would expect – a reassuring and beneficial perspective on yoga. If sentiment analysis reveals a mismatch, like a predominantly negative tone in such an article, it could lead to lower engagement and search rankings, as it doesn’t meet user expectations for such a query.
3. Moderation
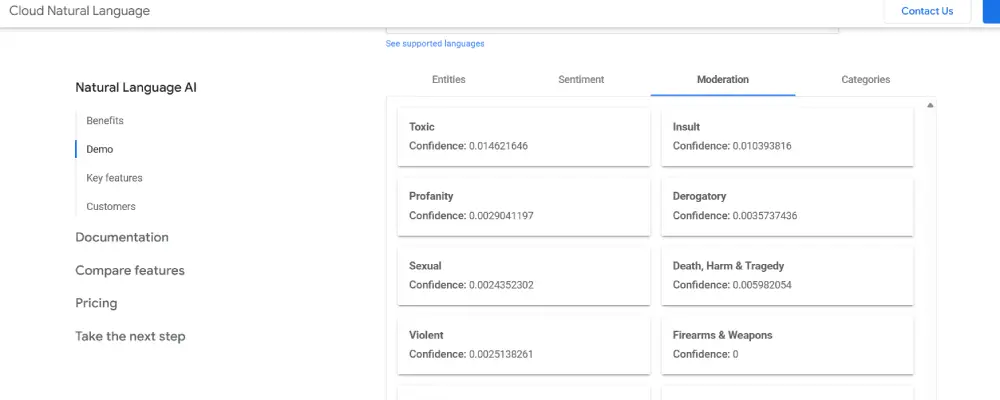
Text moderation examines documents to detect potentially problematic content across several safety categories, including harmful or sensitive subject matter. The analysis checks the text against predefined attributes to identify any portions that may be considered unsafe or inappropriate.
4. Categorization for Content Relevance
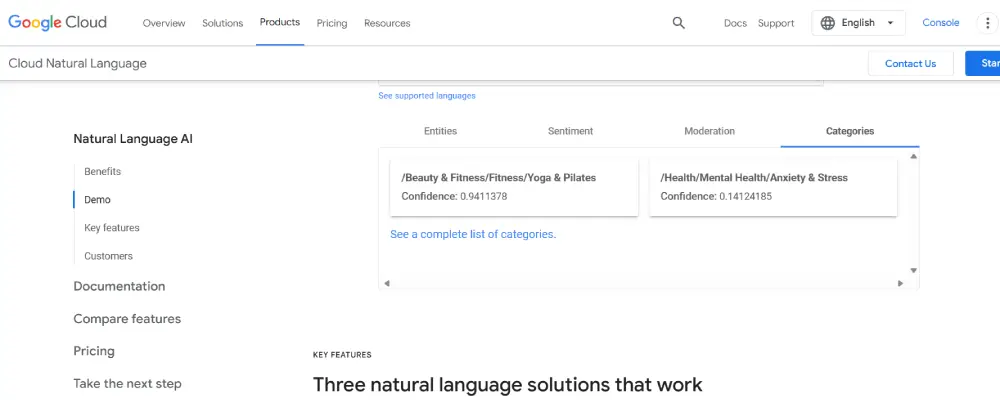
It provides useful information about the category of the content. Effective categorization in SEO involves organizing and labeling content so that it’s easily discoverable and relevant to specific user queries. This process ensures that search engines can accurately understand and index the content, improving its visibility for related searches.
Accurate categorization helps search engines quickly identify the primary and related topics of content, enhancing its match with relevant queries. This can lead to better placement in search results and an improved user experience, as users find the content they’re searching for more easily.
Consider a website with a wide range of articles on health and fitness. If an article specifically focuses on “Low-Impact Cardio Exercises for Beginners,” it should be categorized under broader categories like “Cardio Exercises,” “Fitness for Beginners,” and “Low-Impact Workouts.” Such specific categorization helps search engines index the article accurately for relevant queries. When a user searches for low-impact cardio exercises, the search engine, recognizing the article’s relevance through its categorization, is more likely to present it in the search results.
The Future of SEO with NLP
Looking ahead, the integration of NLP with advanced machine learning and AI technologies is set to redefine SEO. The experts discussed the potential future directions of SEO, highlighting the need for continuous learning and adaptation in this dynamic field.
- Top AI Marketing Tools in 2026 - December 2, 2025
- Best SEO Content Optimization Tools - November 13, 2025
- People Also Search For (PASF): The Complete 2025 Guide to Smarter SEO Optimization - November 11, 2025




